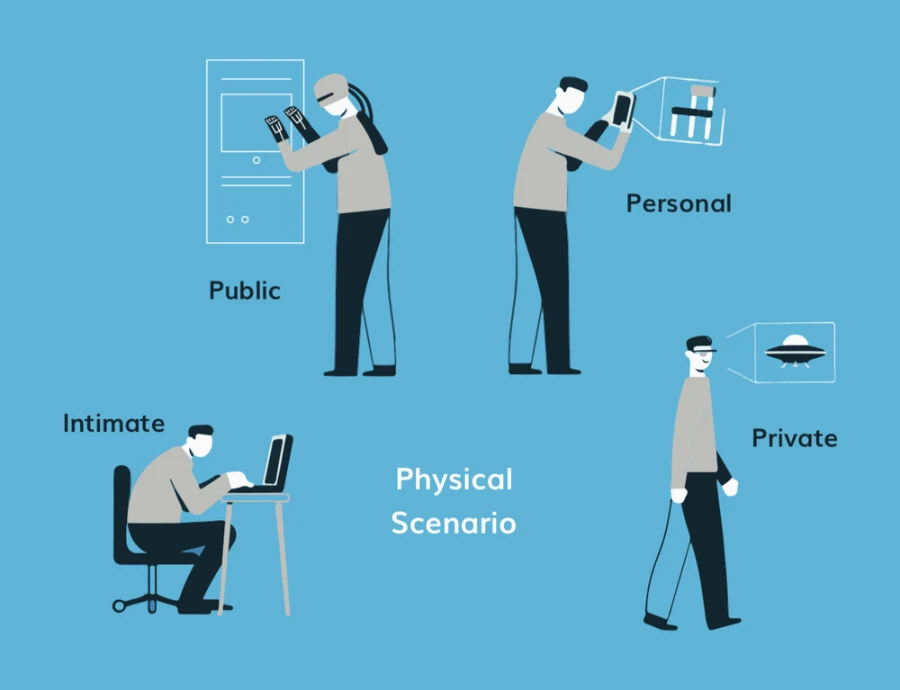
Phone augmented reality apps are not just for entertainment, as many people think. They serve a wide range of purposes, from infotainment and gaming to coding instruction, education and enterprise.
However, in the vast majority of cases, augmented-reality calibration opportunities are lost because they are either hard or expensive to build or due to forgetting oversight.
Types of Apps
Three types of apps can be used for augmented reality calibration: marker-based apps, markerless apps, and location-based apps.
Marker-based apps use a marker, such as a QR code, to calibrate the AR experience. The marker is placed in the environment and used as a reference point for the AR content. This type of app is best suited for controlled environments, such as museums or trade shows.
Markerless apps do not require a marker to calibrate the AR experience. Instead, they use the phone’s sensors (accelerometer, gyroscope, compass) to track the phone’s orientation and position in space. This type of app is best suited for outdoor environments or large spaces where it would be difficult to place a marker.
Location-based apps use GPS to track the phone’s location of specific landmarks or geographic features. This type of app is ideal for outdoor experiences where users are moving around freely.
Things to Consider
There are three main things to consider when calibrating an augmented reality experience on a mobile app: the type of device being used, the operating system of the device, and the specific app being used.
Device Type: The experience will be different depending on whether the user is interacting with the app through a smartphone or a tablet. Make sure to take this into account when calibrating.
Operating System: The way augmented reality is experienced on iOS devices will be different than on Android devices. Make sure to keep this in mind when calibrating for each platform.
Specific App: Each augmented reality app has its specific calibration requirements. Be sure to consult the documentation for the app you’re using to ensure accuracy.
Reality Data Processes in Gaming Apps
When it comes to augmented reality mobile apps, the quality of the experience is largely dependent on how well the real-world data is processed. This is why it’s important to have a clear understanding of the different reality data processes that are used in gaming apps. But, what is calibration parameters in phone
There are generally three different types of real data that can be used in gaming apps: video, images, and 3D scans. Video is captured by the camera on the device and can be used to provide a live view of the environment. Images are typically still photos that are stored on the device or in the cloud. 3D scans are usually more accurate than images and can be used to create a realistic 3D model of the environment.
The first step in processing real-world data is to capture it using one of these three methods. Next, the data needs to be annotated so that it can be interpreted by the app. This annotation process can be done manually or automatically using algorithms. Finally, the app uses this annotated data to understand the real-world environment and overlay digital content accordingly.
It’s important to note that reality data processing is a computationally intensive task. Therefore, it’s crucial to have robust hardware and software capabilities to provide an optimal AR experience for users.
Device & Camera Properties in a Mobile App
When calibrating an AR experience on a mobile device, three key parameters must be considered: the position of the device’s camera, the field of view (FOV) of the camera, and the physical dimensions of the captured image.
The position of the camera is important because it directly affects the size, perspective, and placement of virtual objects in real-world surroundings. To ensure proper calibration, make sure that the camera is in a fixed position and not moving around too much.
The field of view (FOV) of the camera is also an important factor to consider. A wider FOV will result in a larger area being captured by the camera and vice versa. It’s important to select an appropriate FOV that doesn’t cut off too much of the surroundings or distort virtual objects.
Finally, another key parameter to consider is the physical dimensions of the captured image. This includes both the width and height of the image as well as its resolution. A higher resolution will provide more detail but may also require more processing power from the device. Select an appropriate dimension and resolution based on your application’s needs.
Dataset parameters in AR apps
There are many different ways to calibrate an AR application, but the most common method is to use a marker. This marker can be anything from a QR code to a more traditional business card with a logo on it. The marker is placed in the centre of the screen and the user is asked to line it up with the edges of the screen. Once the marker is aligned, the app will take several pictures of it from different angles and use those pictures to calculate the size, shape, and position of the marker on the camera.
After the marker has been placed, the next step is to ask the user to input some basic information about themselves, such as their height and weight. This information is used to calculate things like how far away objects should appear relative to the user’s height. With this information, AR apps can adjust their virtual objects so that they appear at realistic distances and sizes.
Finally, developers need to think about how users will interact with their apps. Will they be using it for navigation purposes? Or will they primarily be looking at static images? The answers to these questions will dictate what kind of calibration process is necessary. For example, if users will be moving around while using an AR navigation app, developers will need to include a way to calibrate compass directionality so that North always points in the right direction.
Source Positions
When calibrating an augmented-reality app for use on a mobile device, three key source positions must be taken into account: the position of the device’s camera, the position of the user’s eyes, and the position of the object being viewed.
The camera’s position is critical for two reasons: first, it needs to be close enough to the object being viewed so that it can track its movements accurately; and second, if it is too far away, the user will experience a sense of disconnection between what they are seeing in the real world and what is being displayed on their device.
The user’s eye position is also important, as it determines how they will see the virtual objects in the real world around them. If the eye position is not correct, it can cause problems with depth perception and make it difficult to interact with virtual objects.
Finally, the position of the object being viewed also needs to be taken into account. This is because the size and placement of virtual objects will appear different depending on where they are located by the viewer. If an object is placed too close to the viewer, it will appear larger than it is; if it is placed too far away, it will appear smaller.
Target Positions
There are many different ways to calibrate an augmented reality (AR) app for mobile devices. Depending on the app and the type of device, the process can vary greatly. However, there are some general tips that all developers should keep in mind when calibrating their AR apps:
1. Target positions: When setting up AR calibration targets, be sure to place them at least 2 meters apart from each other. This will ensure that the app can properly track the device’s movement and position of the targets.
2. Device orientation: Make sure that the device is oriented in a way that is similar to how it will be used during the actual use of the app. This will help ensure the accuracy of tracking and prevent any issues with distorted images
3. Lighting conditions: Try to calibrate in an area with good lighting conditions. too much or too little light can make it difficult for the app to accurately track the device’s position and orientation.
4. Background objects: Be aware of any background objects that may interfere with tracking. If possible, try to calibrate in an area with few nearby objects so as not to cause any inaccurate readings by the app.
Orientation, Scale and Distance Parameters
Three primary factors need to be considered when calibrating an augmented-reality application for mobile devices: orientation, scale, and distance parameters.
Orientation refers to how the device is held about the user’s body. The most common way to hold a mobile device is with the screen facing towards the user, but other orientations are possible and may be more suitable for certain types of applications. For example, holding the device in a landscape orientation may be better for applications that require a wider field of view.
Scale refers to the size of objects about one another. For an augmented-reality application to work properly, it needs to have an accurate understanding of the size of objects in the real world. This can be tricky to accomplish, as size can vary depending on the distance between the object and the viewer.
Distance parameters define how far away from the viewer objects can be before they cease to be visible. This is important for two reasons: first, it ensures that objects do not appear too small or too far away; and second, it prevents objects from appearing in places where they should not be visible (e.g., behind walls).
Photoshop Factors
There are many factors to consider when calibrating an augmented reality mobile application. The first and arguably most important factor is the quality of the camera. A high-quality camera will result in a more realistic experience for the user. Additionally, the size and resolution of the camera’s sensor will affect the overall performance of the app.
Another important factor to consider is the position of the camera on the user’s head. If the camera is too far away from the user, it will be difficult to track their movements and place virtual objects accurately in their field of view. Conversely, if the camera is too close to the user, it may cause discomfort and make it difficult to see clearly.
Finally, lighting conditions must be taken into account when calibrating an AR app. If there is not enough light, tracking accuracy will suffer and virtual objects may appear dark or blurry. However, if there is too much light, glare can become an issue and make it difficult to see virtual objects.
Widget’s position and orientation parameters
There are many factors to consider when determining the position and orientation of widgets in mobile apps. The most important factor is the user’s current surroundings. Other factors include the size and shape of the device, the user’s field of view, and the app’s current context.
When considering the position of a widget, it is important to take into account the user’s current surroundings. If the widget is not visible to the user or if it obscures an important part of the user’s view, it will not be effective. The position of a widget must also be appropriate for the size and shape of the device. Widgets that are too small or too large for the device may be difficult for users to see or interact with.
The orientation of a widget must also be considered when determining its position. The orientation should be such that the widget is easily visible and accessible to the user. If a widget is positioned in an oblique or off-axis orientation, it may be more difficult for users to see or interact with it.
Conclusion
We hope you found our guidelines for augmented-reality calibration in mobile apps helpful. Remember, proper calibration is essential for ensuring a high-quality AR experience for your users. If you have any questions or need help getting started, feel free to contact us. We’re always happy to assist!